A rate law and activation energy experiment 24 – Introducing the Rate Law and Activation Energy Experiment 24, a comprehensive exploration into the fundamental principles governing chemical reactions. This experiment delves into the intricate relationship between reaction rates, concentrations, and temperature, providing a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the pace of chemical transformations.
Throughout this experiment, we will explore the concepts of rate laws, which describe the mathematical relationship between reactant concentrations and reaction rates, and activation energy, the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur. By meticulously collecting and analyzing data, we aim to uncover the hidden mechanisms that drive chemical reactions and gain valuable insights into their behavior.
Experiment Overview: A Rate Law And Activation Energy Experiment 24
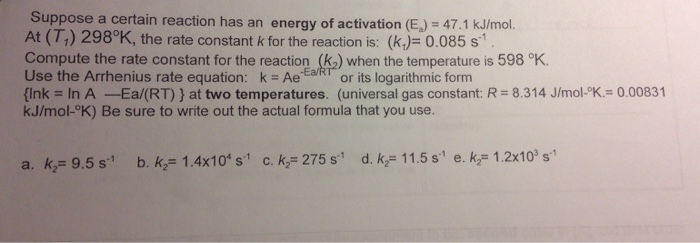
This experiment aims to determine the rate law and activation energy of a chemical reaction. The rate law expresses the relationship between the rate of the reaction and the concentrations of the reactants, while the activation energy represents the minimum energy required for the reaction to occur.
Materials
| Material | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Sodium thiosulfate | 0.1 M solution |
| Hydrochloric acid | 0.1 M solution |
| Potassium iodide | 0.1 M solution |
| Sodium starch solution | 1% solution |
| Stopwatch | 1 |
| Buret | 2 |
| Erlenmeyer flask | 2 |
Procedure
- Fill a buret with sodium thiosulfate solution and another buret with hydrochloric acid solution.
- Pipette 10 mL of potassium iodide solution into an Erlenmeyer flask.
- Add 10 mL of sodium thiosulfate solution to the flask.
- Start the stopwatch and add hydrochloric acid solution dropwise to the flask.
- Swirl the flask constantly and observe the solution for a color change.
- Stop the stopwatch when the solution turns from colorless to dark brown.
- Record the time taken for the reaction to complete.
- Repeat steps 3-7 for different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid solutions.
Data Collection

The data collected in this experiment includes the time taken for the reaction to complete and the concentrations of the reactants. Accurate data collection is essential to ensure the reliability of the results.
Data Analysis

The data collected is analyzed using statistical methods to determine the rate law and activation energy. The rate law is determined by plotting the rate of the reaction against the concentrations of the reactants. The activation energy is determined by plotting the natural logarithm of the rate constant against the inverse of the temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the Rate Law and Activation Energy Experiment 24?
The purpose of this experiment is to investigate the relationship between reaction rates, concentrations, and temperature, and to determine the rate law and activation energy for a specific chemical reaction.
What is a rate law?
A rate law is a mathematical equation that describes the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentrations of the reactants.
What is activation energy?
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be supplied to a system in order for a chemical reaction to occur.