Conductor sizes are expressed in the nec in or in – Conductor sizes are expressed in the National Electrical Code (NEC) in inches or millimeters, and they play a crucial role in electrical system design and safety. This article explores the NEC standards for conductor sizes, their impact on current capacity and voltage drop, and their applications in various electrical installations.
Conductor Sizes: NEC Standards: Conductor Sizes Are Expressed In The Nec In Or In
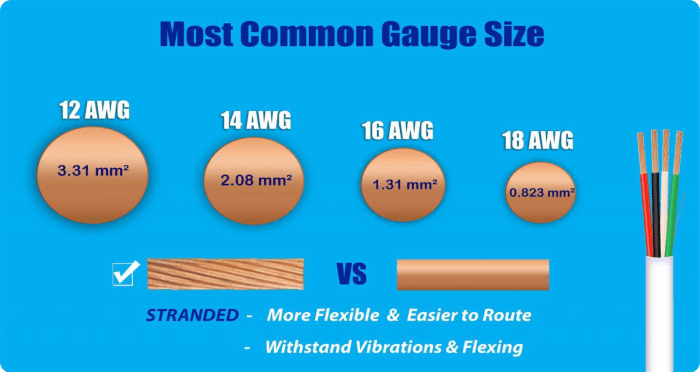
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for the safe installation and use of electrical conductors. One of the key aspects of NEC compliance is the proper sizing of conductors to ensure they can safely carry the intended current without overheating or causing voltage drop.The
NEC specifies conductor sizes using two different designations: AWG (American Wire Gauge) and kcmil (thousand circular mils). AWG is a logarithmic scale used for smaller conductors, while kcmil is used for larger conductors. The higher the AWG or kcmil number, the smaller the conductor size.
Conductor Sizes: Current Capacity
The size of a conductor directly affects its current-carrying capacity. Larger conductors can safely carry more current than smaller conductors. The NEC provides tables that specify the maximum allowable current for different conductor sizes and materials. Exceeding the recommended current capacity can lead to overheating, insulation damage, and increased risk of fire.
Conductor Sizes: Voltage Drop, Conductor sizes are expressed in the nec in or in
Conductor size also impacts voltage drop. Smaller conductors have higher resistance, which causes more voltage drop over a given distance. This can be a significant concern for long circuits or circuits carrying high currents. The NEC requires that voltage drop be limited to a maximum of 5% for branch circuits and 3% for feeders.
Conductor Sizes: Material and Insulation
Conductors are typically made of copper or aluminum. Copper has higher conductivity than aluminum, so a smaller copper conductor can carry the same current as a larger aluminum conductor. The type of insulation used on a conductor also affects its size.
Thicker insulation provides better protection against electrical shock and environmental factors, but it also increases the overall diameter of the conductor.
Conductor Sizes: Applications
The appropriate conductor size for an electrical application depends on several factors, including the current demand, voltage drop requirements, and environmental conditions. For example, larger conductors are typically used for high-current applications, such as main feeders or distribution panels. Smaller conductors may be sufficient for low-current applications, such as lighting circuits or control wiring.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of conductor size in electrical systems?
Conductor size is crucial because it affects the amount of current a conductor can safely carry and the voltage drop that occurs along its length.
How does conductor size impact current capacity?
Larger conductor sizes have lower resistance, allowing them to carry more current without overheating.
What is the relationship between conductor size and voltage drop?
Smaller conductor sizes have higher resistance, which leads to greater voltage drop over a given distance.
What factors influence the selection of conductor size for a specific application?
Factors include the amount of current to be carried, the voltage drop that can be tolerated, and the environmental conditions.

