JPRS in NFPA 1033 are written to provide guidance on the development and implementation of Joint Procedures for Response to Hazardous Materials Incidents.
These procedures are essential for ensuring the safety of responders and the public during hazardous materials incidents. They provide a framework for coordinating the actions of multiple agencies and organizations, and they help to ensure that resources are used effectively.
JPRS Background and Purpose
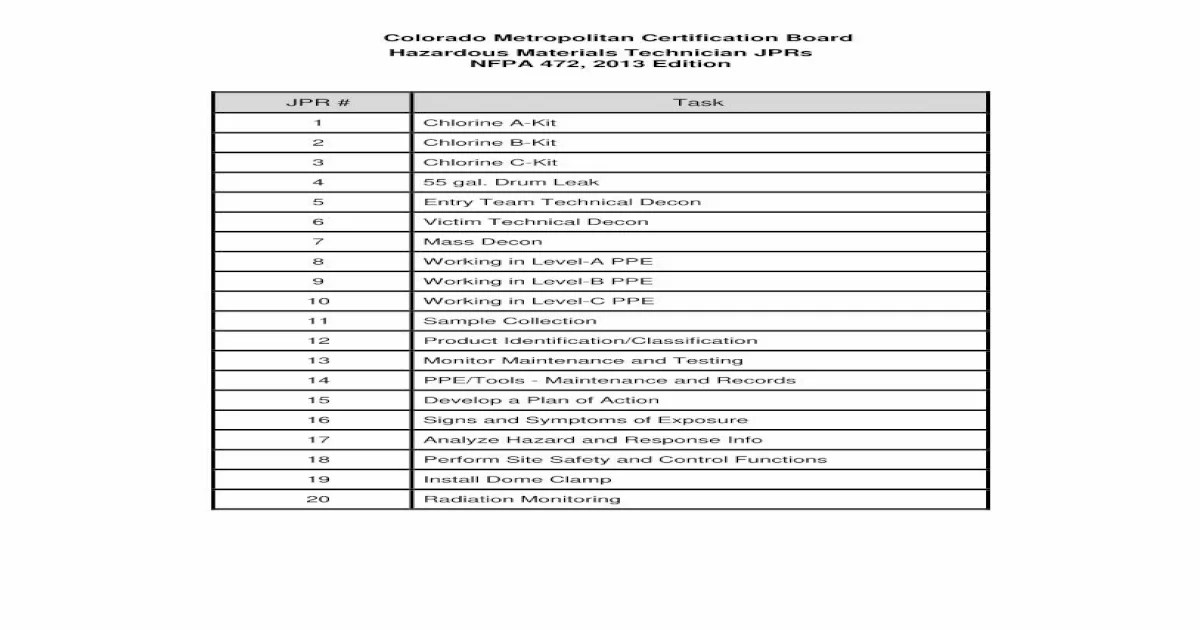
The Joint Proficiency and Readiness System (JPRS) is a collaborative initiative established under NFPA 1033, the Standard for Professional Qualifications for Fire Inspector and Plan Reviewer.
The JPRS was developed to address the need for a standardized system to assess and certify the competency of fire inspectors and plan reviewers. The system was created through a collaborative effort involving representatives from fire service organizations, code enforcement agencies, and industry stakeholders.
JPRS Development Process
The JPRS development process involved several key steps:
- Identification of core competencies for fire inspectors and plan reviewers
- Development of assessment tools to measure proficiency in these competencies
- Establishment of a certification process to recognize individuals who meet the required standards
Key Components of JPRS

JPRS is a complex system composed of various essential components that work together to achieve its objectives. Understanding the roles and relationships among these components is crucial for ensuring effective implementation and operation of the JPRS.
The key components of JPRS include:
- Incident Commander (IC): The IC is responsible for overall management of the incident and has the authority to make decisions and allocate resources.
- Joint Information Center (JIC): The JIC is responsible for coordinating and disseminating public information about the incident.
- Public Information Officer (PIO): The PIO is the primary spokesperson for the incident and is responsible for communicating with the media and public.
- Joint Operations Center (JOC): The JOC is the central coordination point for all operational activities during the incident.
- Unified Command (UC): The UC is a group of senior-level officials from multiple agencies who share responsibility for incident management.
These components work together closely to ensure that information is shared effectively, decisions are made quickly, and resources are allocated efficiently. Coordination and communication among these components is essential for the success of the JPRS.
JPRS Implementation: Jprs In Nfpa 1033 Are Written

Effectively implementing a JPRS requires careful planning, training, and evaluation. By following these steps and incorporating best practices, organizations can ensure a successful implementation that meets their specific needs and goals.
Planning
- Identify the specific goals and objectives for implementing a JPRS.
- Assess the current state of preparedness and identify areas for improvement.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that Artikels the steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Secure buy-in and support from leadership and all stakeholders.
- Establish a governance structure to oversee the implementation and ensure accountability.
Training
- Provide comprehensive training for all personnel involved in the JPRS.
- Cover topics such as JPRS concepts, roles and responsibilities, and operational procedures.
- Incorporate hands-on exercises and simulations to enhance understanding and practical skills.
- Develop training materials and resources that can be used for ongoing reference.
- Conduct regular training updates and refreshers to ensure knowledge retention.
Evaluation
- Establish metrics and indicators to measure the effectiveness of the JPRS implementation.
- Conduct regular assessments to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders and use it to refine the JPRS as needed.
- Document lessons learned and best practices to inform future implementations.
- Continuously evaluate and update the JPRS to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Benefits of JPRS
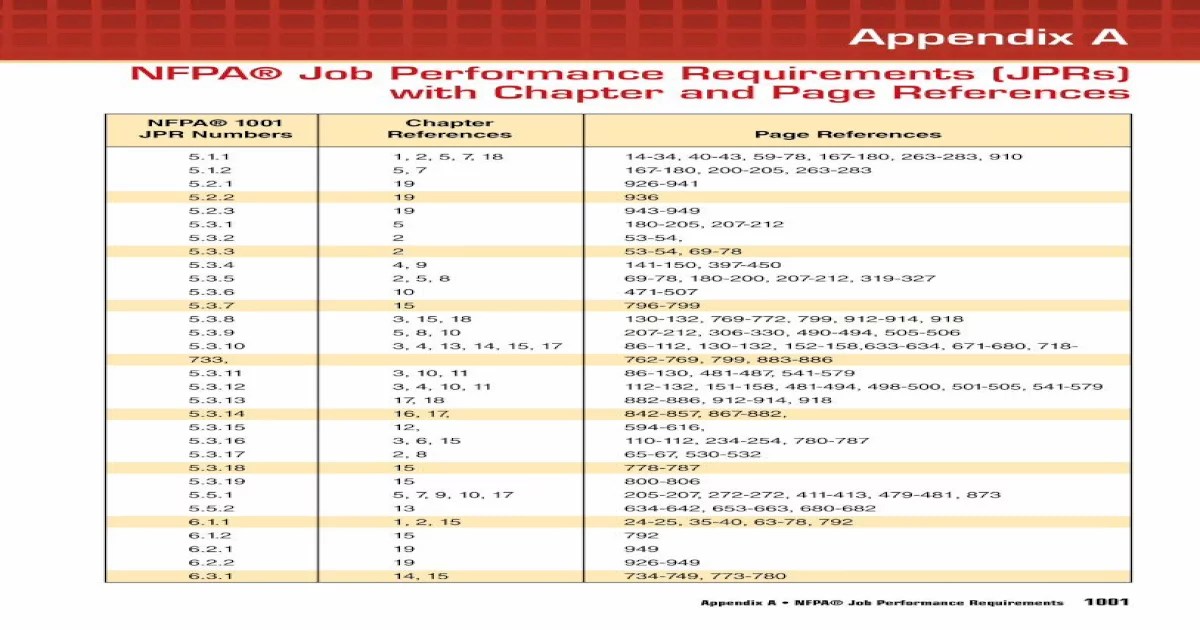
Implementing JPRS can yield numerous benefits for organizations, including enhanced safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Improved safety is a primary advantage of JPRS. By standardizing and streamlining job planning and risk assessment processes, JPRS helps organizations identify and mitigate potential hazards more effectively. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of incidents and accidents, ensuring a safer work environment for employees.
Case Study: Reduced Incident Rates
A manufacturing facility implemented JPRS and experienced a significant reduction in incident rates. Over a two-year period, the facility saw a 25% decrease in recordable injuries and a 40% decrease in lost-time accidents. This improvement was attributed to the comprehensive risk assessments and enhanced communication facilitated by JPRS.
JPRS also contributes to increased efficiency by optimizing job planning and resource allocation. By standardizing processes and eliminating redundancies, JPRS helps organizations streamline operations and reduce wasted time. This improved efficiency leads to increased productivity and cost savings.
JPRs in NFPA 1033 are written in a straightforward manner, providing clear guidance on fire safety. For those interested in exploring the fundamentals of biology, I highly recommend the Biology by Raven 13th Edition . This comprehensive textbook offers an in-depth understanding of biological concepts, complementing the practical insights provided by JPRs in NFPA 1033.
Case Study: Improved Project Completion Times
A construction company implemented JPRS on a large-scale project and noticed a significant improvement in project completion times. By leveraging JPRS to plan and coordinate tasks effectively, the company was able to reduce project delays and complete the project ahead of schedule, resulting in cost savings and increased customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, JPRS supports compliance with industry regulations and standards. By providing a systematic approach to risk assessment and job planning, JPRS helps organizations demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory compliance. This can reduce the risk of fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
Challenges and Limitations

Implementing JPRS can present certain challenges and limitations that need to be acknowledged and addressed. These challenges may arise due to various factors, including resource constraints, organizational readiness, and technological limitations.
Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive approach, involving careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By understanding the potential challenges and developing strategies to mitigate their impact, organizations can ensure the successful implementation and effective utilization of JPRS.
Resource Constraints
Implementing JPRS may require significant financial and human resources. Organizations need to carefully assess their resource availability and ensure that adequate funding and staffing are allocated to support the implementation and ongoing operation of JPRS.
Strategies for addressing resource constraints include:
- Prioritizing JPRS implementation based on the organization’s most critical needs and available resources.
- Seeking external funding or partnerships to supplement internal resources.
- Leveraging technology to automate tasks and reduce the need for manual labor.
Organizational Readiness
Successful JPRS implementation requires a high level of organizational readiness. This includes having a clear understanding of the JPRS concept, its benefits, and the potential impact on the organization’s operations.
Strategies for enhancing organizational readiness include:
- Conducting thorough training and education programs for all stakeholders involved in JPRS implementation.
- Establishing a clear communication plan to keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the implementation process.
- Creating a culture of continuous improvement and feedback to ensure that JPRS is effectively meeting the organization’s needs.
Technological Limitations
JPRS implementation may be limited by technological constraints, such as legacy systems, data compatibility issues, and cybersecurity concerns.
Strategies for overcoming technological limitations include:
- Investing in technology upgrades and infrastructure to support JPRS implementation.
- Developing data integration strategies to ensure seamless data exchange between JPRS and other systems.
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect JPRS data and systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Future Developments and Innovations

As JPRS continues to evolve, we can expect several exciting developments and innovations that will further enhance its effectiveness. These advancements will leverage emerging technologies and industry best practices to improve incident response coordination, situational awareness, and resource management.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence, Jprs in nfpa 1033 are written
AI-powered tools can automate various JPRS functions, such as data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling. This integration will enable real-time monitoring of incident data, providing responders with actionable insights and early warnings. AI can also assist in resource allocation, optimizing the deployment of personnel and equipment based on predicted needs.
Enhanced Interoperability
Improved interoperability between JPRS and other emergency management systems is crucial. Future developments will focus on seamless data sharing and collaboration among multiple agencies and jurisdictions. This will enable a more coordinated response, eliminating communication barriers and ensuring a unified approach to incident management.
Mobile and Cloud-Based Accessibility
The increasing adoption of mobile devices and cloud computing offers opportunities to enhance JPRS accessibility. Mobile applications will allow responders to access critical information and communicate with each other in the field. Cloud-based platforms will provide secure and reliable data storage, enabling real-time updates and collaboration from anywhere.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
JPRS will increasingly leverage data analytics to support data-driven decision-making. Advanced data visualization tools will provide responders with clear and actionable insights into incident patterns, resource utilization, and performance metrics. This data-centric approach will enable evidence-based decision-making and continuous improvement of JPRS.
Answers to Common Questions
What are JPRS?
JPRS are Joint Procedures for Response to Hazardous Materials Incidents.
Why are JPRS important?
JPRS are important because they provide guidance on the development and implementation of procedures for coordinating the actions of multiple agencies and organizations during hazardous materials incidents.
How can I get a copy of JPRS?
You can download a copy of JPRS from the NFPA website.